Zimbabwe
Making history
Where does the Resurrection plant come from?
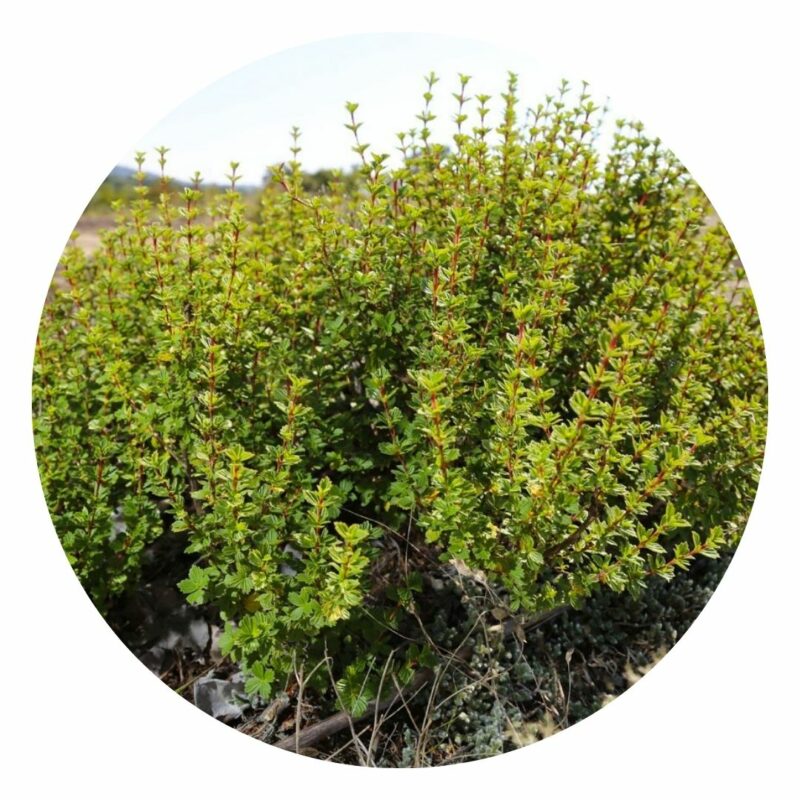
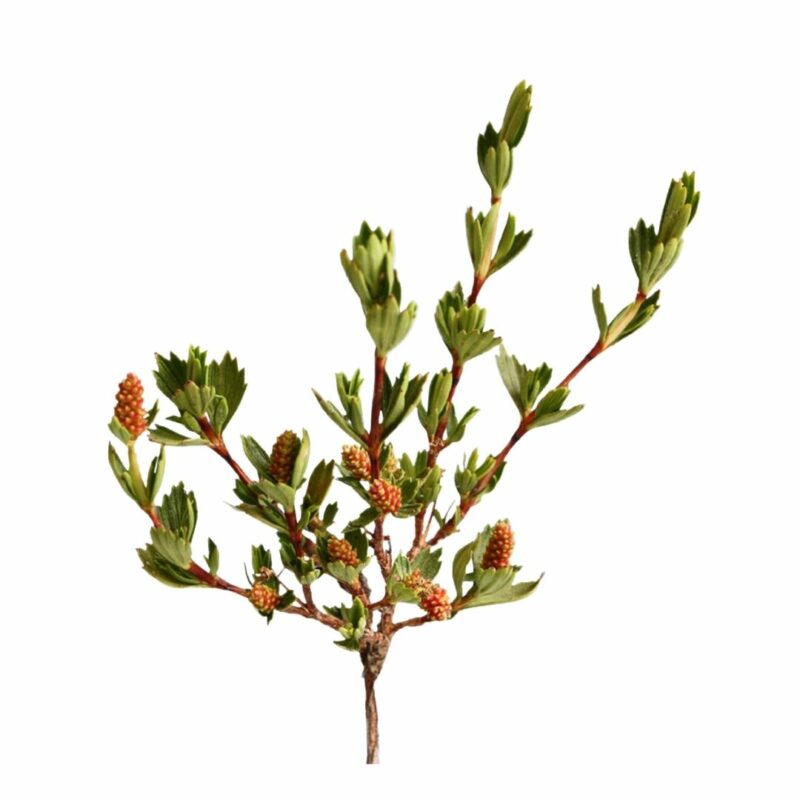
Resurrection bush is a woody shrub with tough branches. For most of the year it looks like an upright bundle of red-brownish sticks, no more than 30-50cm high. It is called resurrection bush for the speed with which apparently dead leaves revive when the rains come.
The resurrection bush is very widespread in Zimbabwe. It is found only in shallow soil over rock, crevices and rocky hillsides where few other plants survive, in full sun, usually between 900-1,200m.
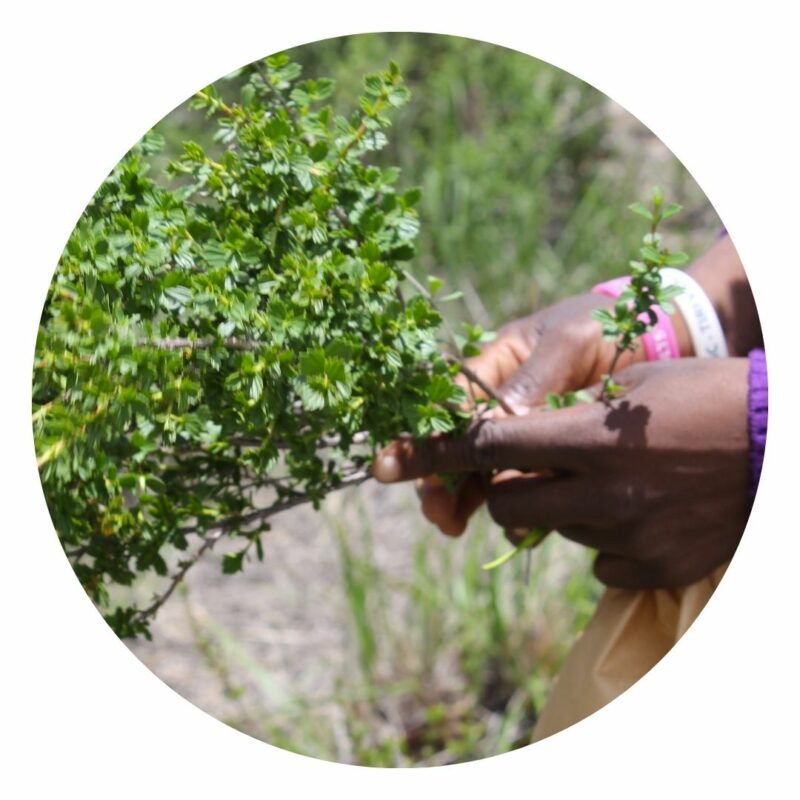

Harvesting time
Collection is done between May and September, after the rains. Harvesting can also be done during short dry spells during the wet season, when the plant has dehydrated.
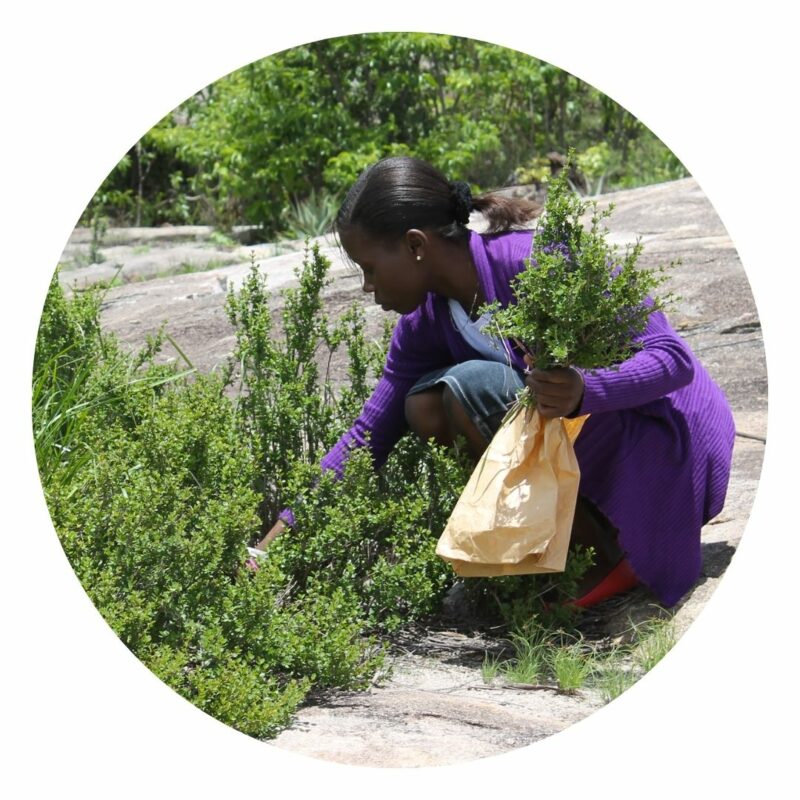

Average yield
Where abundant, 20-30 kg can be collected for the tea market in a day. Although a farmer can only harvest about 10 kg of good quality sticks per day, prices paid for these are much higher.

Markets
Informal trade in Zimbabwe exists through herbalists and across borders. Formal trade is to herbal tea processors, but is very small. Export opportunities exist also for cosmetic extract production.
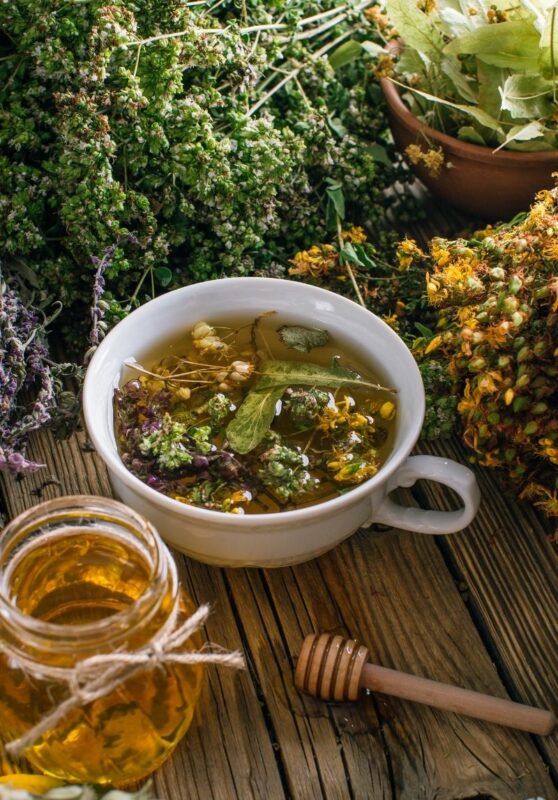


A study comparing resurrection bush tea to rooibos tea found that resurrection bush tea has antioxidant properties comparable to rooibos. Resurrection bush tea is a rich source of phenolic compounds which act as antioxidants and strong inhibitors of the oxidative stress arising from exhaustion and other body reactions like phospholipid peroxidation (a leading factor in premature aging). It also contains arbutin, a potent antiseptic (also known to have skin-lightening activity).
Its essential oil exhibits strong antibacterial and antifungal activities.
The leaves are mostly used as a traditional medicine to treat a variety of ailments. Inhalation of smoke from burning leaves treats chest complaints and asthma. Decoctions (herbal or iced tea) treat coughs, influenza, mastitis, backache, kidney disorders, haemorrhoids and abdominal pains, scurvy, menstrual pain, hypertension, halitosis and gingivitis.
Resurrection bush also has potential as an essential oil for use in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic and perfume industry.
Resurrection plant
Diagram of components
Arbutin
Not common in vascular flora, especially not in conjunction with Trehalose. Commonly found in plants that tend to undergo severe stress. Source of hydroquinone. Limits peroxidation, which causes damage to the cell, of the unsaturated lipids, a component of plant cells.
Step 03:
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Trehalose
Not commonly found in vascular flora. Plays a key role in protecting the cell membrane, allowing cells to wholly rehydrate. Potential for use in a wide range of products, most noticeably in skincare.
Tannins and Polyphenols
Tannin levels are much higher in dry plants because as it desiccates, the tannins strengthen. Its immunity to fungal infections in its dry state highlights the high tannin levels. The high tannin levels protect the elasticity in the cell walls so that they remain intact during desiccation. The high tannin levels also make it unpalatable to animals (yet still delicious as an aromatic tea)
Trehalose
Not commonly found in vascular flora. Plays a key role in protecting the cell membrane, allowing cells to wholly rehydrate. Potential for use in a wide range of products, most noticeably in skincare.

Arbutin
Not common in vascular flora, especially not in conjunction with Trehalose. Commonly found in plants that tend to undergo severe stress. Source of hydroquinone. Limits peroxidation, which causes damage to the cell, of the unsaturated lipids, a component of plant cells.
Tannins and Polyphenols
Tannin levels are much higher in dry plants because as it desiccates, the tannins strengthen. Its immunity to fungal infections in its dry state highlights the high tannin levels. The high tannin levels protect the elasticity in the cell walls so that they remain intact during desiccation. The high tannin levels also make it unpalatable to animals (yet still delicious as an aromatic tea)

Trehalose
Not commonly found in vascular flora. Plays a key role in protecting the cell membrane, allowing cells to wholly rehydrate. Potential for use in a wide range of products, most noticeably in skincare.
Arbutin
Not common in vascular flora, especially not in conjunction with Trehalose. Commonly found in plants that tend to undergo severe stress. Source of hydroquinone. Limits peroxidation, which causes damage to the cell, of the unsaturated lipids, a component of plant cells.
Tannins and Polyphenols
Tannin levels are much higher in dry plants because as it desiccates, the tannins strengthen. Its immunity to fungal infections in its dry state highlights the high tannin levels. The high tannin levels protect the elasticity in the cell walls so that they remain intact during desiccation. The high tannin levels also make it unpalatable to animals (yet still delicious as an aromatic tea)
Did you know
What makes our product unique?

Skin rejuvenation
Revive your skin with our anti-ageing product, which contains Myrothmnus Flabellifolius, the resurrection bush.

Essential minerals
Our products are high in antioxidants and antimicrobials, protecting your body from infection and disease.

Sustainable and eco-friendly
Everything from the harvesting processing to our packaging is kind to the earth and has future generations in mind.







